RollApps
- RollApps may start as tokens and evolve into fully fledged lightning-fast blockchains.
- RollApps have the ability to bootstrap liquidity before launch.
- Rollapp Creators earn royalties and endorsements based on their Rollapp popularity.
- Rollapps come with pre-built primitives to support AI, Oracles and RNG use-cases.
- RollApps come with a frontend framework to allow for singless user experience from both mobile and web.
- Rollapps operation is fully decentralized.
- RollApps are desgined to be cost efficient and lightning fast. :::
Overview
In their final form, RollApps are lightning-fast blockchains that leverage Dymension’s Layer 1 for security, user access, and liquidity. However, in the Dymension ecosystem, a RollApp doesn’t necessarily start that way.
Initially, a RollApp can be launched as a token to bootstrap liquidity. Later, it can evolve into a fully fledged blockchain.
The Dymension RollApp primitive opens the door for every creator, technical or not, to launch their own crypto venture, whether it be a game, AI agent or DeFi protocol, and earn royalties and endorsements with minimal barriers to entry.
Key Personas
Creators
Creators are the ones who actually create the RollApp. They set the initial RollApp metadata, tokenomics, Bootstrap liquidity conditions and choose initial operator.
Creators of the RollApp are eligible for royalties and endorsements which is mostly based on their Rollapp popularity.
Operators
Operators manage nodes called sequencers which validate, order, and process transactions. Unlike other popular RAAS, Rollapp operation on dymension is fully decentralized.
The importance of operation decentralization is crucial to avoid operators holding your rollapp hostage.
Operators may choose to run a RollApp based on the economic viability (e.g., Sequencer rewards).
Development and Operation
RollApp Development Kit
Dymension supports various virtual machines and custom execution environments. New execution environments may be added as explained in the Dymension RollApp Standards. Dymension currently supports the following VMs:
Dymension Connect
Dymension Connect is a frontend framework for dymension rollapps which allows developers to easily integrate signless UX (aka quick auth), wallet connect, cross-chain transfers and more.
Roller
Roller is a tool that allows you to easily deploy and operate a RollApp. It also comes packed with three pre-built primitives:
- Defi Orcale
- RNG
- AI Oracle
Blueprints
Blueprints are pre-built RollApps that are ready to be deployed on Dymension. They showcase how to use the roller primitives and dymension-connect, and build invincible RollApps. The blueprints repo contains currently three blueprints:
- Defi - Simple Binary Option App
- Coin Flip - Simple Coin Flip App
- Guess The Number - Simple AI Agent PVP Game
How It Works - Overview
At a configurable period the Sequencer batches produced blocks and submits them to the DA. After receiving a response from the DA network that the published data was accepted, the Sequencer then publishes a state update containing the state roots of the block together with other metadata to Dymension Hub. With data published onchain, The Dymension Hub may then verify any fraud proof submission.
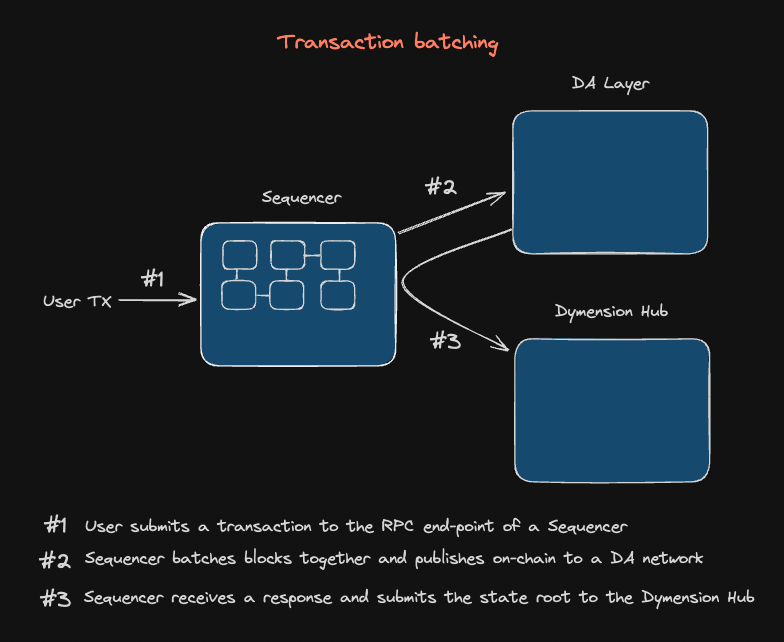
RollApps utilize Dymint to process transactions and network the created blocks. Dymint only produces blocks when necessary (on-demand block production) and by that greatly reduces operating costs.